Boundary Condition Editor#
The boundary condition editor is used to define the inflow and outflow boundaries. The data is written to the INFLOW.DAT and OUTFLOW.DAT files.
Inflow Boundary Condition Editor#
Any number of inflow hydrographs to the FLO-2D model can be assigned to channel, floodplain or even the 1-D street component. This represents a flood inflow to the flow domain from an off-site source.
Inflow Node#
To create a point of inflow, click the Add Point BC button on the Boundary Condition Editor widget.
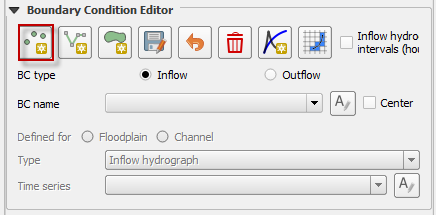
Digitize the inflow node by left clicking the location of the inflow node on the map. In this example, the inflow node is a channel inflow node. It is not necessary to enter the fid. Click OK to create the feature.
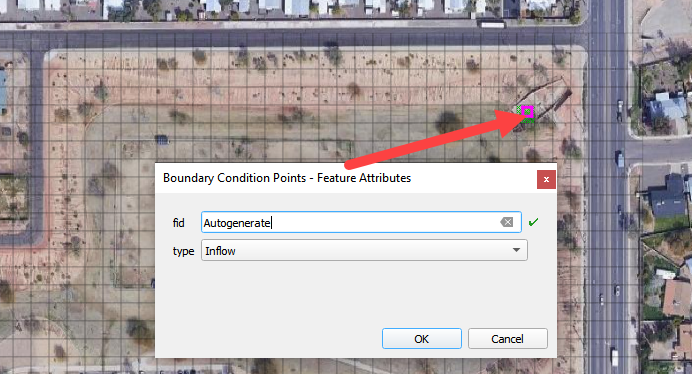
Click the Save Button to load the data into the editor.
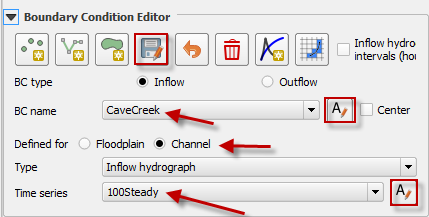
Assign the conditions to the inflow node as seen in the following image.
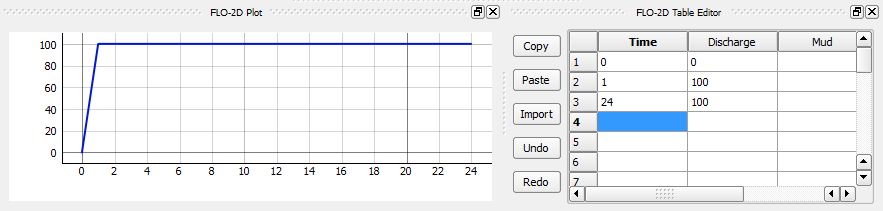
This example inflow node will have a steady hydrograph with 100 cfs assigned to Cave Creek inflow node.
The time series inflow hydrograph is assigned in the table editor where time is in hours and discharge is cfs or cms. This is a clear water inflow hydrograph and no sediment concentration is assigned.
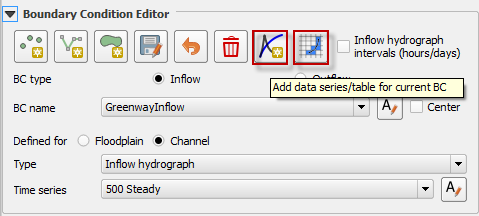
Repeat the process to add additional inflow hydrographs. Use the Add data series/table for current BC button to create a new hydrograph.
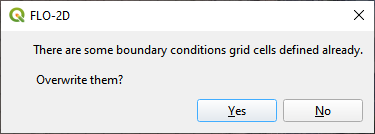
Use the Schematize button (shown below) to save the data to the Schematic Layers and click Yes to overwrite the layers.
Outflow Boundary Conditions#
Boundary outflow conditions include:
Normal depth control
Stage time control
Stage discharge control
These conditions define how the channel or floodplain discharge enters or leaves the FLO-2D model domain.
Outflow Floodplain#
Normal depth boundary
This is an outflow condition where the flow leaves the domain without effecting the upstream water surface elevation, select the outflow nodes along the downstream boundary or along the edge of a grid system.
Click the Add Polygon BC button

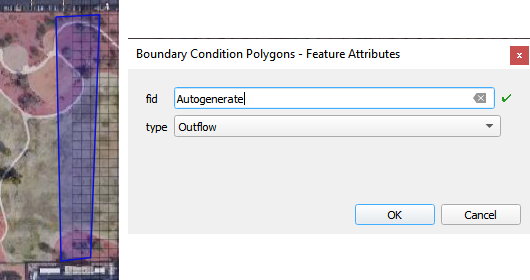
Digitize a polygon that covers the desired boundary extent. Right click the last vertex to close the polygon.
Set the type to Outflow and click OK.
Click Save to load save the load the data into the BC Editor.
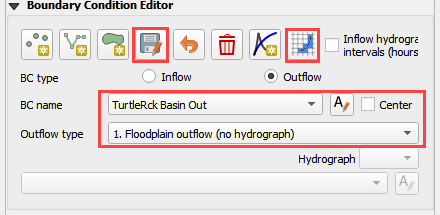
Name the boundary and set the outflow type to 1. Floodplain outflow (no hydrograph).
Click the Schematize button (shown below) to complete the boundary.
Outflow Channel#
For channel outflow at a normal depth condition, use the channel outflow node on the downstream boundary or channel segment terminus.
Click add a point boundary and click the last left bank channel node.
Click Save.
Name the feature.
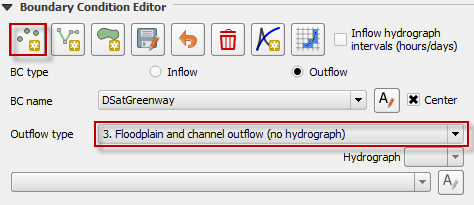
Set the outflow condition for the channel to 3. Floodplain and channel outflow (no hydrograph).
Note that only one point is required.
Click the Schematized button.
Outflow with Hydrograph#
Multiple Domain System
Use this option with any floodplain boundary that will transfer flow between two domains.
See the Multiple Domain Flow Exchange Training Package for further instructions:
Click the Add Polygon BC button and draw a line through the desired outflow nodes.
Click Save to load save the feature to the layer and activate the editor.
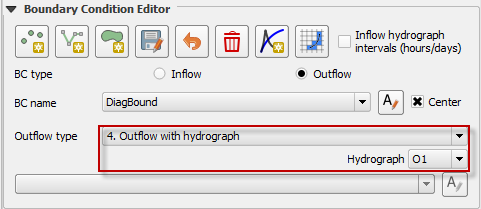
Name the boundary condition and set the boundary Outflow type conditions as Outflow with Hydrograph.
Outflow with Time – Stage Hydrograph for Floodplain#
To represent variable time-stage boundary conditions such as:
Tides
Storm surge
Tsunamis
Flooding from a large river
The time–stage relationship can be synchronized with rainfall and upstream watershed flooding. Select the outflow nodes along the downstream boundary with a polygon.
Click the polygon BC button.
Digitize the polygon across the boundary.
Click Save to save the feature to the layer and activate the editor.
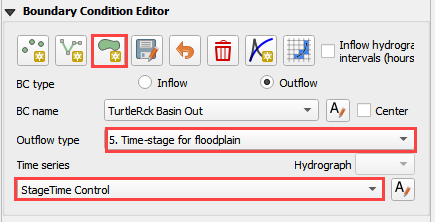
Name the boundary and set the boundary conditions.
Name and fill the Time Series table.
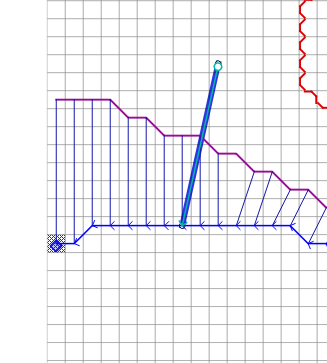
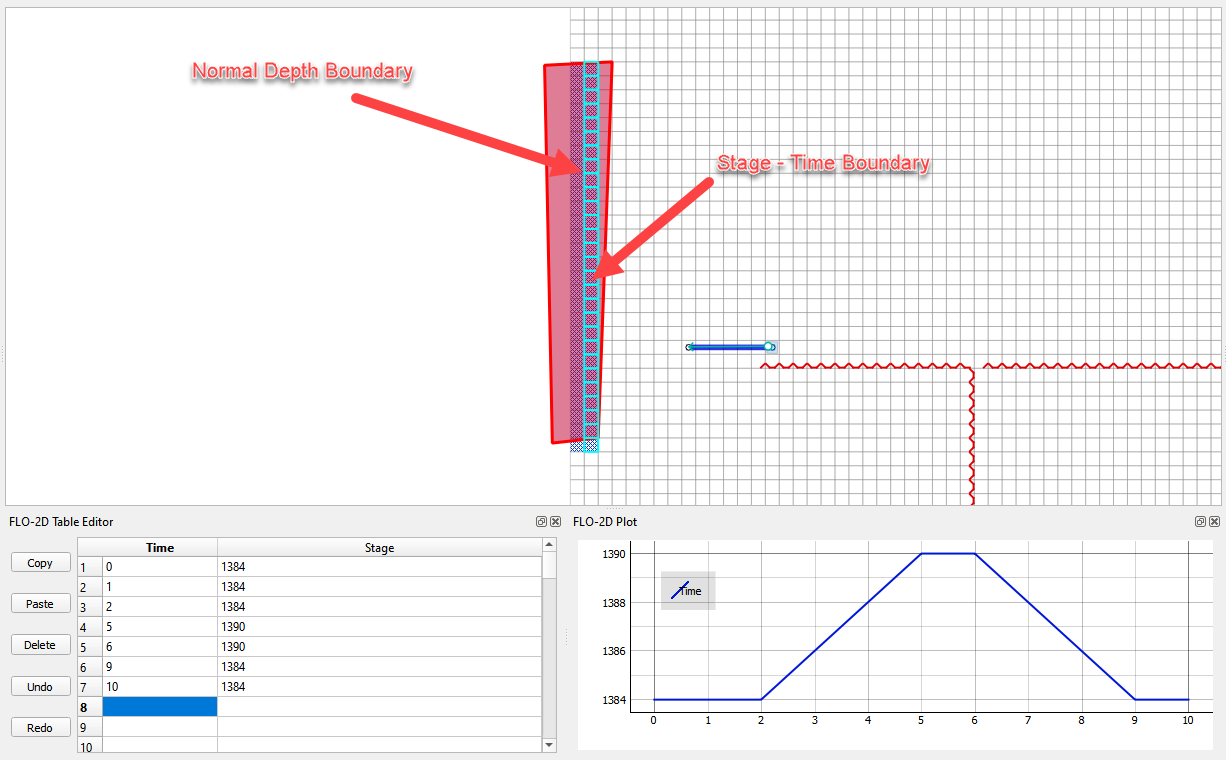
In the figure below, there are two sets of outflow nodes.
The Normal Depth nodes allow water that exceeds the Stage to cross the outflow boundary. This allows rainfall accumulation or inflow hydrograph accumulation to leave the boundary.
The Stage – Time nodes apply a water surface elevation. This water can fill the downstream area up to the stage.
Outflow with Time – Stage Hydrograph for Channel#
Like the time-stage condition for the floodplain select this option to represent ocean tide, storm surge, tsunamis, or flooding from a large river control in a channel terminus. The time – stage relationship can be synchronized to rainfall and watershed flooding.
Select the standard outflow node at the end of the channel.
Set the time-stage node one element upstream.
Click Save to load save the feature to the layer and activate the editor.
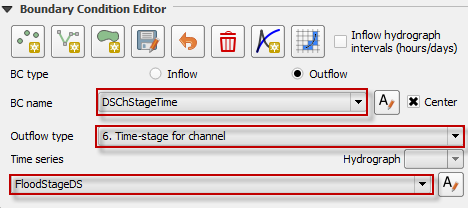
Name the boundary and set the boundary conditions.
Name and fill the Time Series table.
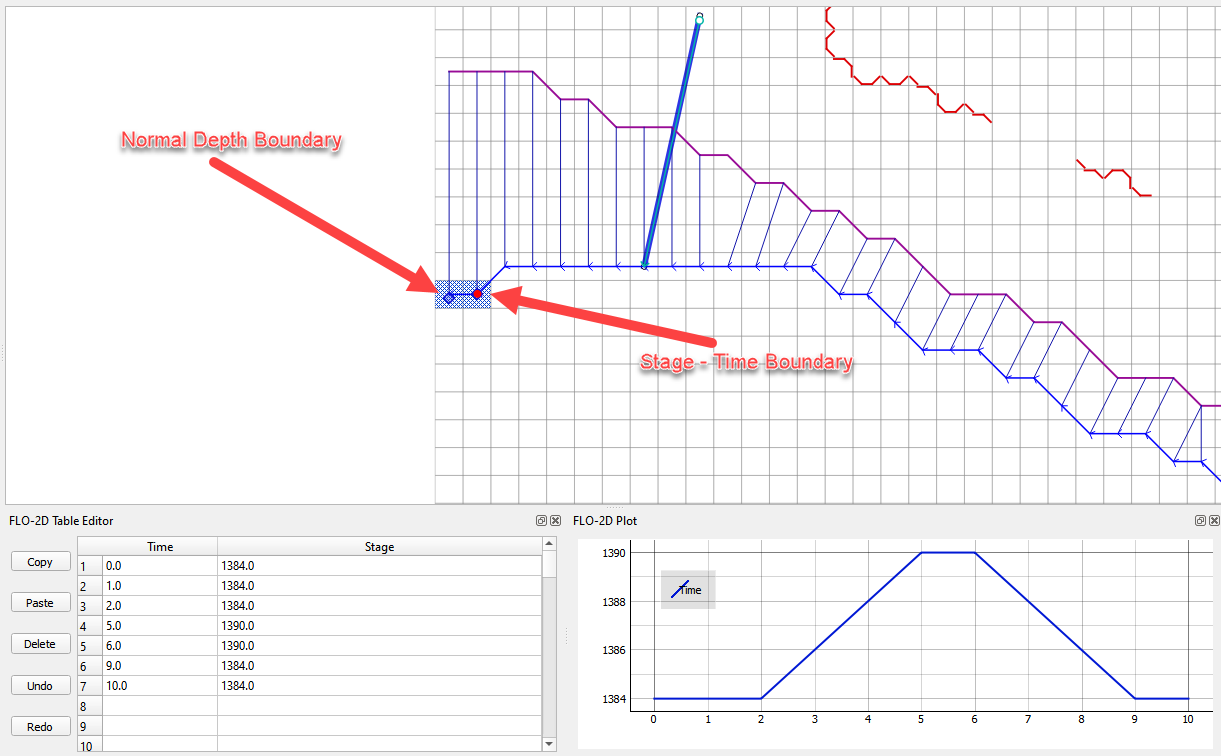
Time-Stage for Floodplain and Free Floodplain and Channel#
Use this option to set the stage of a downstream elevation control. This node will allow water to collect on the boundary until it can exceed the stage at the boundary. It can be used for two purposes.
Anytime there is a control on the boundary that releases water at a known stage.
Set the elevation for matching the water surface elevation of an existing FEMA map.
Set this up with the same method described in the previous two sections.
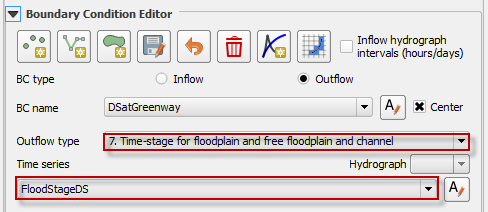
Time-Stage for Channel and Free Floodplain and Channel#
This option is the same as option 7 with the condition that the stage – time table is assigned to the channel instead of the floodplain.
Set this up with the same method described in the previous two sections.
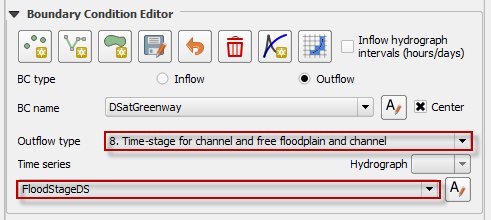
Channel Stage-Discharge Parameters#
This outflow option defines the discharge from a channel based on the stage using rating curve. Several rating curves can be assigned for multiple limiting depths. This system is used when there is a control or a gage at the channel with a known stage-discharge relationship.
Select the stage-discharge node at the end of a channel segment.
Click Save to load save the feature to the layer and activate the editor.
Name the boundary and set the boundary conditions.
Name and fill the Q(h) parameters table.
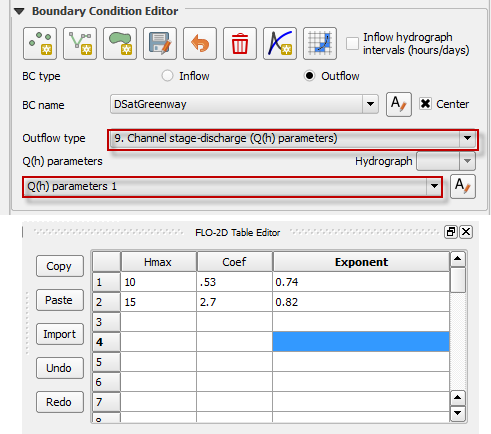
Channel Stage-Discharge (Q(h) table)#
The final outflow option is used to define the downstream boundary with a stage-discharge table.
Select the stage-discharge node at the channel terminus.
Click Save to load save the feature to the layer and activate the editor.
Name the boundary and set the boundary conditions.
Name and fill the Q(h) table.
Troubleshooting#
The most common problems with creating outflow.dat data is caused by creating conflicts by putting other components in the outflow grid elements.
The schematic layers and tables will reset each time the Schematize tool is used. This could cause overwriting of imported data. Convert the Boundary Conditions to User Layers for projects that are imported into QGIS before performing the schematization process.
If the data does not export correctly, check the tables. The tables can be edited directly or can be copied into an OUTFLOW.DAT file.
Saving and restarting might resolve some issues with the GeoPackage but check the layers attributes prior to restarting QGIS.
If a Python Table Update error appears, Delete the QGIS folder from AppData/Roaming and rebuild the QGIS Profile.