9. TOL Spatial#
The spatially variable TOL parameter is specified depth below which no discharge is shared between grid elements. This FLO-2D parameter represents grid element depression storage and can be used to simulate Low Impact Development (LID) storage such as the volume in cisterns or infiltrated volume through permeable pavers.
In the following example, the neighborhood collects rainwater using built-in cisterns that are attached to the gutters of the buildings. The cisterns have a fixed volume and there is one per building. The volume of each cistern is 50 gallons or 6.68 ft3. Divide this volume by the surface area of a grid element to determine the TOL depth value assigned to each cell.
Digitize or Copy Data#
Click the Tolerance Areas layer and use the editor tool to digitize the outline of the building roof area. This is the area that collects water.
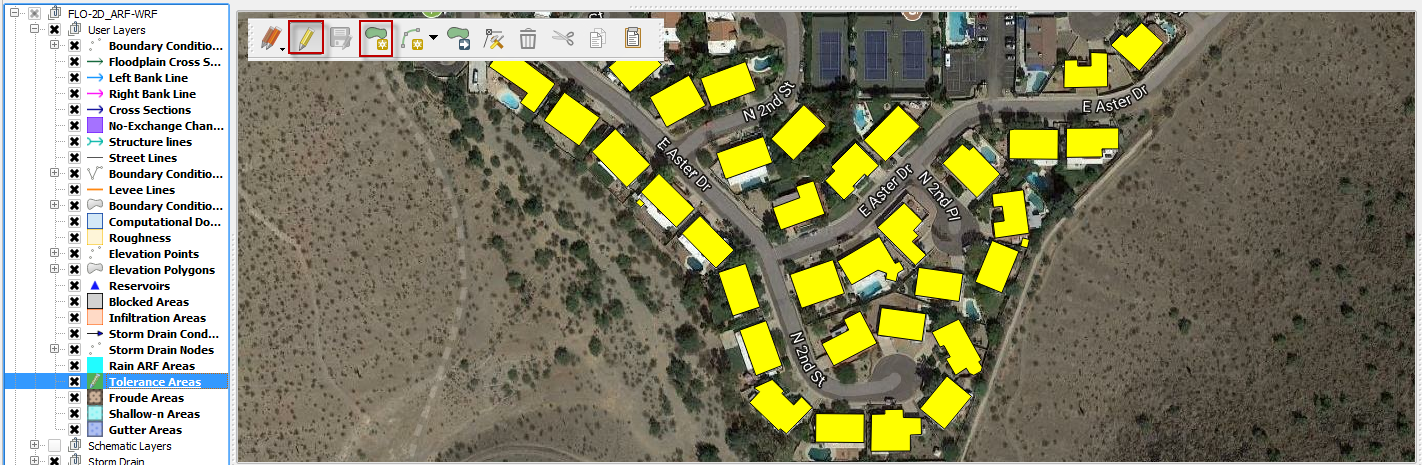
The roof polygons can be imported to a separate layer and pasted into the Tolerance Areas layer. In this instance, the polygons were copied from the Blocked Areas layer.
In this example the LID TOL value is unknown and must be calculated from the cistern volume and the collection area. Each house has a theoretical 50-gallon rain collection cistern. The volume is converted to 6.68 cubic feet. The tolerance value is a depth in feet, so it can be applied to the roof area of each house. For the sake of simplicity, the assumption is that the roof area and the house polygon area are the same.
Define the Tolerance Attribute#
Open the attribute table of the Tolerance Areas layer.
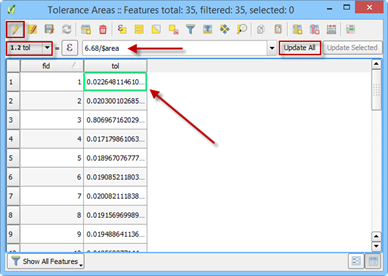
On the attribute table window, click on the Toggle Editing button, change the field to TOL, add the command to set the TOL depth (6.68 / $area) and click Update All.
Save and close the editor tool and close the attribute table. This process converted the volume of the cistern to a depth over the area of each polygon.
Sample Data#
Click the Sample Spatial Tolerance Values button.

Once the process is complete, Click OK to complete TOL the assignment.
This process has converted the volume from the polygon to the grid elements that intersect the polygon.
Troubleshooting#
Create the tolerance polygons if they are missing from the Tolerance Areas layer.
If the Grid layer is empty, create a grid and try again.
If a Python error appears during the sampling process, the attribute table may be missing. Save and reload the project into QGIS and try again.
If the Attribute Fields: collapse, calc_arf, and calc_wrf are not filled by the user, the calculation cannot be performed.
